For easybill, differential taxation is an almost daily topic. Time and again, our support team hears that other providers do not support differential taxation. But why is that? What is the challenge of this taxation and what does it mean to sell goods with differential taxation?
A brief overview
Definitionssache Differenzbesteuerung
Differential taxation, also known as margin taxation, is regulated in Section 25a of the German Value Added Tax Act (UStG). It always comes into play when used items, works of art, antiques or collectibles are resold. It is therefore relevant when, for example, a dealer buys an antique table from a private individual and then resells it to one of his customers.
The differential taxation should therefore be known above all to dealers (so-called resellers) who trade in used items or sell them at auction. So especially for online traders the differential taxation can be relevant under certain conditions. The aim of this type of taxation is that goods do not have to be fully taxed again for which VAT has already been paid once (at the time of purchase). Do you meet the requirements for differential taxation? Then you only have to pay tax on the difference between the sales price and the purchase price.
The requirements for the differential taxation
You are considered a reseller under tax law if you are an entrepreneur and trade in movable tangible property on a commercial basis – such as the table mentioned in the example above. You are also considered a reseller if you sell goods at public auction. Another requirement? You must have purchased the goods in Germany or another country belonging to the EU.
The differential taxation does not apply if you use the goods privately. You may not apply this type of taxation if, for example, you buy a used laptop and use it privately. The differential taxation may only be applied to goods that you use professionally or with which you trade. In tax law, this is referred to as a “paid delivery for business”.
And the last requirement for you to be allowed to apply the margin scheme is that the seller of the goods is not entitled to deduct input tax. Because that would mean that he can reclaim the VAT for the original purchase price from the tax office. However, if you then only pay tax on the difference between the purchase and sales price, the tax authority would waive the sales tax.
From practice for practice
Does it all sound a bit complicated? Then let’s take a look at a concrete example of how margin taxation works.
The classic area of application for the differential taxation is the trade with used cars. Let’s assume you work as a used car dealer and find a nice car while you are on vacation in Spain. The car is sold by a private person. This person is therefore not entitled to deduct input tax. For 5,000 euros you buy the car from this private person and hire a freight forwarder to pick up the car and drive it to your dealership.
After minor cosmetic repairs, you resell the car for 8,500 euros. Since you bought the car from a private person in the Community (EU) and you are a reseller yourself, you may apply the margin scheme.
In concrete terms, this means that you only have to pay tax on the difference between the sales price and the purchase price. So this means: 8,500 euros (sales price) – 5,000 euros (purchase price) = 3,500 euros
And the usual sales tax of 19 percent, i.e. 665 euros, is due on this 3,500 euros.
No differential taxation possible
On the other hand, differential taxation is excluded for items that do not belong to tangible goods. This means that you cannot apply differential taxation to software that you purchase second-hand for your business, as software is not a tangible item.
In addition, there are items that do belong to tangible goods, but are nevertheless excluded from differential taxation. These include precious metals as well as precious stones (for example sapphires, diamonds, rubies, etc.) and also imitation or synthetically produced precious stones. If you are active in this sector, you should urgently consult your tax advisor as to what options you have here.
Differential taxation via onlineshop
You sell above mentioned goods via your own online shop? The most common store systems on the market should already be able to map this form of taxation. The shopping cart of your customers should already show 0% VAT if an item is sold with differential taxation. If this is not the case or your store system does not support differential taxation, you need an alternative. easybill users can breathe a sigh of relief at this point, because of course we already have the solution up our sleeve.
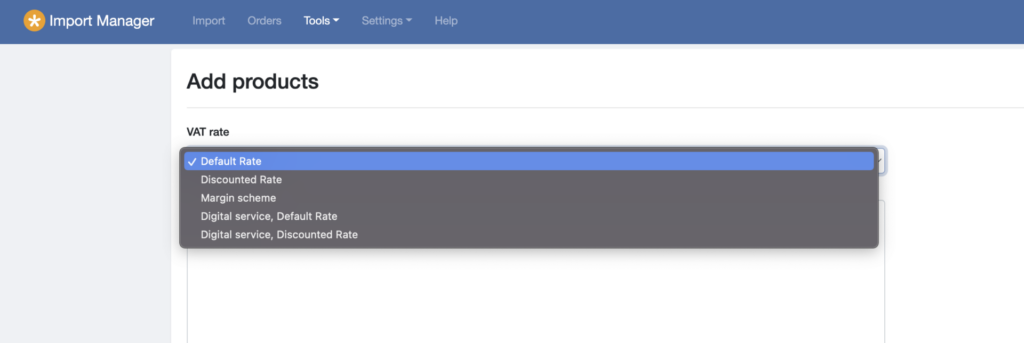
With our intelligent product database of the Import Manager, you as a seller define which items are shown with differential taxation. Thus, you do not need to worry if your store system only outputs the gross price. easybill takes over the correct tax display of your differential taxation with all associated information of the paragraph.